Character Motivation Elements in The Wizard of Oz
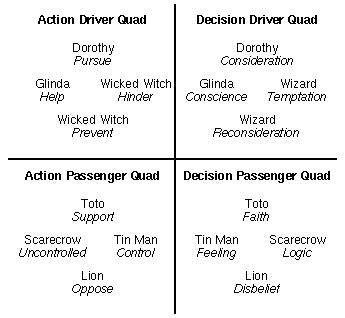
In looking at these patterns, the Passenger Characters in The Wizard of Oz seem very much like the Passenger Characters in Star Wars, with that one notable exception of the “flipping” of Logic and Feeling in relation to Control and Uncontrolled. In other words, the two Characters simply traded places on one Dynamic Pair of Elements in a single Quad. It makes sense that a stereotypical Reason Character would be logical AND controlled, and a stereotypical Emotion Character would be feeling AND uncontrolled. But if you simply flip the Action Characteristics in relation to the Decision Characteristics, far more versatile Characters are created — characters whose approach is no longer in complement to their attitude, but in conflict with it. In a sense, these Characters are made more interesting by creating an inequity within them even as they continue to represent methods of problem solving within the Story Mind.
Looking at the Wizard and the Wicked Witch we see that the other kind of swapping of characteristics also creates much less stereotypical Characters. Rather than a tempter, the Wicked Witch becomes a completely action-oriented pest not only trying to prevent Dorothy from achieving her goal, but hindering her every step on the way as well. The Wizard becomes a purely decision-oriented tempter who represents taking the apparent easy way out while also (through his fearsome reputation, embodiment, and requests) urging Dorothy and her friends to reconsider their decisions. This lack of action characteristics may help explain why the Wizard is so obviously absent during most of the story, although his influence is felt throughout. Obviously, the nature of the combinations of characteristics has a great impact on which decisions and actions the audience will expect and accept from a Character.
From the Dramatica Theory Book