The 12 Essential QuestionsEvery Writer Should Answer
9. Overall Story Throughline
Every story is set against the issues which arise from a single problem. The problem itself will fall into one of four broad categories. If you want the problem to grow out of a situation, then choose Situation; if you want the problem to emanate from an activity, then choose Activity. If you want the problem to evolve from fixed attitudes and states of mind, then choose Fixed Attitude; and if you want the problem to result from the characters’ manipulations and ways of thinking, then choose Manipulation.
Overall Story Throughline: The scenario against which a story takes place.
An author cannot successfully make an argument promoting a solution until he or she has identified the Problem. In stories, Problems can be identified as falling into four broad categories: Situations, Activities, States of Mind, and Manners of Thinking.
These categories are named by the four Classes, Situation (a situation), Activity (an activity), Fixed Attitude (a state of mind), and Manipulation (a manner of thinking).
Situation represents an External State
Activity an External Process.
Fixed Attitude is an Internal State
Manipulation an Internal Process.
Since they are related, all four of these Classes will figure in every story as the Problem works its influence into all areas of consideration. However, only one Class will ultimately prove to be both the source of the Problem’s roots and therefore the place it must ultimately be solved.
The Overall Story Throughline is the throughline which describes how all of the story’s characters have been brought together. By choosing this Throughline, the author sets the background against which the story will be told. Therefore, its influence is gently felt throughout the story.
A SITUATION story deals with an unacceptable situation – one in which the external environment is seen as problematic. This could be a job situation with poor working conditions, being trapped in a sunken ship, waking up as someone else, living next to an orphanage that keeps you awake at night with its screaming waifs or any other intolerable state of affairs. Often, the best way to see a Situation Overall Story is in terms of the Types below the Class of Situation: The Past, How Things are Changing, The Future, and The Present. These Types will be of primary importance to all the Overall Characters in a Situation Overall Story.
An ACTIVITY story employs an activity that needs to arrive at a solution. This might be the effort to steal the crown Jewels, win the love of your heart’s desire, make the Olympic team, or raise the money to buy the orphanage and evict all the screaming waifs. Note that if the existence of the orphanage is the focus of the story, it is a Situation (Situation) Throughline. However, if the effort to buy it is the focus, it is a Activity (Activity) Throughline. Often, the best way to see a Activity Overall Story is in terms of the Types below the Class of Activity: Doing, Gathering Information, Understanding, and Obtaining. These Types will be of primary importance to all the Overall Characters in a Activity Overall Story.
In a like manner, the Fixed Attitude Throughline reflects a state of mind and the Manipulation Throughline describes a mental activity (or manner of thinking). Fixed Attitude Throughline stories might be about prejudice, a lack of self-worth (if it is a fixed view), or a refusal to see the value of someone’s desires. Remember that, as an Overall Story Throughline, these fixed states of Mind will be the source of the problems that everyone in the Overall Story deals with. This would be an Overall view of problems of fixed states of mind, and not looking at how it feels to have these fixations. Often, the best way to see a Fixed Attitude Overall Story is in terms of the Types below the Class of Fixed Attitude: Memories, Impulsive Responses, Innermost Desires, and Contemplation. These Types will be of primary importance to all the Overall Characters in a Fixed Attitude Overall Story.
A MANIPULATION Throughline supports stories where people take too many risks, are egocentric, or make light of serious situations. Overall Stories of this Throughline will look at the effect of a person’s or persons’ thinking in these ways to manipulate others. Placing the Overall Story in this Throughline means in essence that the story will objectify Manipulation, taking an Overall view of these ways of thinking and their effects. The problems that everyone in the Overall Story deals with will come from ways of thinking and their manipulations. Often, the best way to see a Manipulation Overall Story is in terms of the Types below the Class of Manipulation: Developing a Plan, Playing a Role, Changing One’s Nature, and Conceiving an Idea. These Types will be of primary importance to all the Overall Characters in a Manipulation Overall Story.
As a final note, it is important to keep in mind that stories are often not about a problem that exists but a desire to be fulfilled. Stories of this nature can create a much more positive feel as exemplified in a Situation story in which an heiress must spend a million dollars in 24 hours to inherit 30 million more, a Activity story where a mountaineer hopes to be the first to scale a mountain on Mars, a Fixed Attitude story of unconditional love, or a Manipulation story about overcoming a dependence on sedatives. The choice of Throughline narrows the playing field of a story. Without actually putting up walls, choosing a Throughline shifts the focus of audience attention by establishing the center around which broad scale dynamics will revolve. The Dramatica engine is calibrated to this center.
To illustrate the differences between throughline classes, let’s consider how different story concepts might be illustrated in each of the four perspectives:
Overall Story Throughlines that deal with a Situation
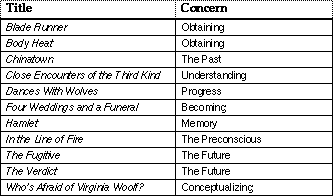
All of the characters are concerned with maintaining or demolishing a situation (e.g. The Verdict or The Fugitive). For example, a country under the thumb of an authoritarian dictator; the condition of a dysfunctional family; a utopian society; a submarine trapped under the ice; progress in one-sided relationships; a murder that occurred 30 years ago; the future of gay rights; the forces that bring on an ice age.
Overall Story Throughlines that deal with an Activity
All of the characters are concerned with an activity or endeavor (e.g. Star Wars or Blade Runner). For example, searching for lost treasure; engaging in a sport; exercising as a way of life; self-flagellation; taking part in a cattle drive; learning about DNA; obtaining secret plans; understanding messages from space, etc.
Overall Story Throughlines that deal with a Fixed Attitude
All of the characters are concerned with a fixed aspect of the mind (e.g. Hamlet or The Client). For example, a community’s firm belief in the occult; a family’s commitment to the memory of its ancestors (ancestor worship); TV addiction; a culture’s fixation on celebrities; a Martian’s prejudice against humans; unthinking responses to the conditions of war; essential desires and drives, etc.
Overall Story Throughlines that deal with Manipulations
All of the characters are concerned with a mental process or manner of thinking (e.g. Who’s Afraid of Virginia Woolf? or Four Weddings and a Funeral). For example, curing a mental illness; determining why someone’s relationships always fail; becoming a new person; being more responsible to the environment; working through childhood trauma; mass manipulation through propaganda; a group of young people coming of age; a team’s creative effort to work out an idea; people pretending to be things they are not, etc.